Mission
Die FLuorescence EXplorer (FLEX) Mission wird globale Daten der Chlorophyllfluoreszenz von Vegetation messen, welche Hinweise auf die photosynthetische Aktivität und den Gesundheitszustand von Pflanzen geben. Diese Informationen sind grundlegend, um den globalen Kohlenstoffkreislauf besser zu verstehen und genauer zu charakterisieren. Damit können Entwicklungen in der Landwirtschaft unterstützt werden und zur Ernährungssicherheit beigetragen werden.
Deshalb wurde FLEX im Jahr 2015 als achte Earth Explorer Mission des Europäische Raumfahrtagentur (ESA) Living Planet Programms ausgewählt ( mission selection report). FLEX wird zusammen mit der Coperincus Sentinel-3 Mission im Tandem fliegen, damit die Daten der OLCI und SLSTR Instrumente zur Interpretation der FLEX-Daten beitragen können.
Daten zu FLEX:
- Start: 2026
- Trägerrakete: Vega-C
- Missionsdauer: 3,5 Jahre
- Größe: 1,5 x 1,2 x 1,2 m (LxBxH), nach ausfalten der Solarpaneele 5,2 m Breite
- Satellitenmasse: 460 kg (davon 140 kg Instrumente, 30 kg Treibstoff)
- Orbit: sonnensynchron, in 814 km Höhe, Inklination 98,64°
- Überflugrate: 27 Tage
- Räumliche Auflösung: 300 m
- Räumliche Abdeckung: Global; Landoberflächen zwischen 56° S und 75° N
- inkl. Inseln mit einer Fläche von 100 km² oder mehr und Küsten mit einer Ausdehnung von 50 bis 300 km
Instrument:
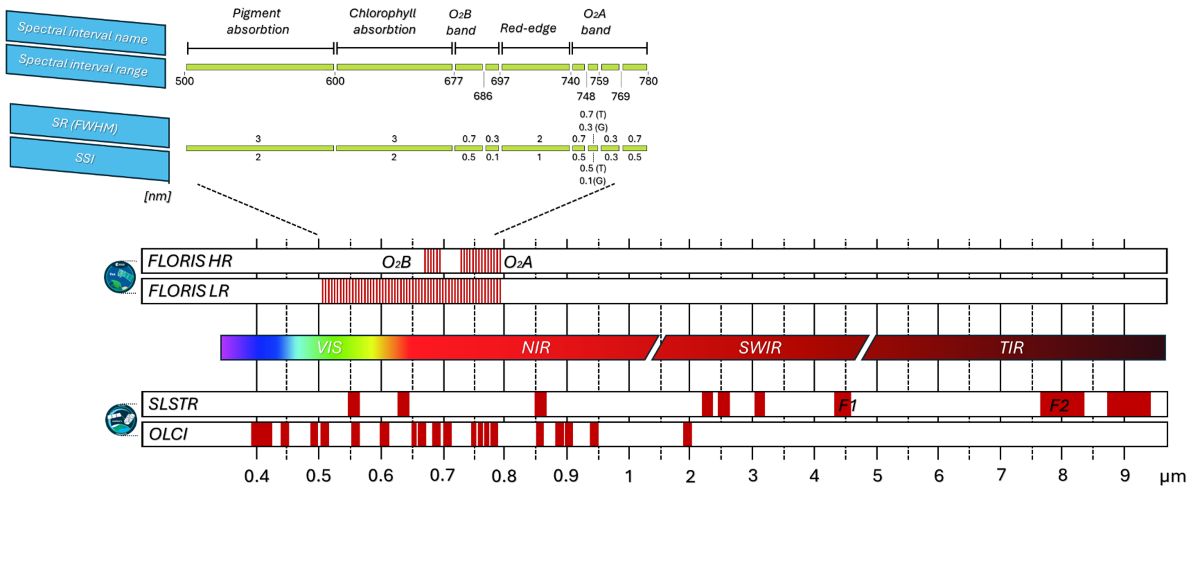
Das Fluorescence Imaging Spectrometer (FLORIS) ist ein hyperspektraler Zeilenscanner im einem Spektralbereich von 500-780 nm mit 0.1 nm spektralem Sampling in den Sauerstoffabsorptionsbanden (759-769 und 686-697 nm) und 0.5-2 nm in den Bändern des Red-Edge, der Chlorophyllabsorption und im Bereich des photochemischen Reflektionsindex (PRI).
FLEX-Datenprodukte
ℹ Die Liste der unten angegebenen Datenprodukte basiert auf den aktuell verfügbaren Dokumenten und wird regelmäßig aktualisiert.
L1C
TOA radiance
Products for FLORIS, OLCI, and SLSTR, as well as a synergy product that is projected on common grid. [1]
L2A - L2 Atmospheric products
TOC radiance + irradiance
Atmospherically corrected top-of-canopy values + cloud screening included for FLORIS. [1]
L2B - L2 Fluorescence products
L2C - L2 Vegetation products
LAI
Leaf area index (LAI) is defined as the one-sided green leaf area per unit ground surface area (leaf area/ground area, m²/m²). LAI changes with species composition and phenology and provides information about canopy structure and functional characteristics of vegetation cover. It is retrieved through a combination of Gaussian process regression (GPR) and a 1D radiative transfer model. Thus, the retrieved LAI is the effective LAI, which does not account for leaf clumping. It can be used in Beer-lambert models e.g. used in GPP estimation. [6]
fAPAR
Fraction of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation (fAPAR) [m-2 s-1] is calculated as the fraction of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR; the solar radiation reaching the surface at 400-700 nm) that is absorbed by vegetation. [6]
LCC
Leaf chlorophyll content (LCC) [µg m-2] controls leaf optical properties and is directly linked to fluorescence emission. It is used for the retrieval of CO2 flux. LCC is representative for the pixel footprint and is likely lower that the mean LCC of all scences in one pixel. [6]
LCARC
Leaf carotenoid content (LCARC) [µg m-2] provides the total carotenoid content and is relevant to understanding photosynthesis, especially in phenology studies. [6]
APAR_ch
Absorbed photosynthetically active radiation by chlorophyll (APAR_ch) [m-2 s-1] is the amount of blue-sky APAR (blue sky = under the mix of diffuse/direct light) absorbed by chlorophyll a + b pigments. [6]
LST
Land surface temperature (LST) will be derived from the Sentinel 3 SLSTR instrument with an uncertainty of ±1 K (G) and of ±2 K (T). [1]
FQE
Fluorescence quantum efficiency (FQE) is defined here as the effective FQE at canopy level. That means it is the probability that a PAR photon absorbed by chlorophyll is re-emitted as a fluorescence photon. It can be described as the ratio of the emitted fluorescence (spectrally and hemispherically integrated and corrected for (re-)absorption) over aPAR_chl. [6]
Fesc
Fluorescence escape probability (Fesc) is defined as the ratio of TOC fluorescence (in observation direction times pi) divided by the fluorescence radiance produced in the canopy by chlorophyll. It is provided spectrally resolved. [6]
RED
Proxy of reversible energy dissipation (RED) [photon m-2 s-1] describes the probability (the so-called yield) that APAR is dissipated as heat through collective reversible mechanisms that plants use to protect themselves from excessive illumination. [6]
ETR
Electron transport rate (ETR) [electrons m-2 s-1] s the rate by which excited electrons travel to the reaction centers of photosystems. It here is defined as the product of the photochemical yield (phiP) and fAPAR_chl. In a first attempt it will be calculated from APAR_chl, LST and FQE. [6]